AstroLogics Tutorial, Boolean Network Analysis and Clustering : Bonesis Tutorial#
This tutorial demonstrates the AstroLogics framework for analyzing and comparing Boolean network model ensembles. AstroLogics is designed for benchmarking Boolean models through three major evaluation criteria: network evaluation, logical function evaluation, and dynamic evaluation.
Overview of AstroLogics Framework#
AstroLogics addresses a critical gap in Boolean network modeling: while multiple methods exist for Boolean model synthesis (like Bonesis, BN-sketch), there hasn’t been a standardized way to evaluate and compare generated model ensembles. The framework focuses on:
Dynamic properties: Examining state transition graphs and model behaviors through simulation
Logical function evaluation: Analyzing and comparing logical rules that govern node behaviors
Model clustering: Identifying groups of models with similar dynamics and logical features
Required Libraries#
import pandas as pd
import os
import astrologics as ast
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from zipfile import ZipFile
Dataset: CNS Differentiation Model#
We’ll use the Central Nervous System (CNS) differentiation model from Qiu et al., 2017, which serves as the tutorial network for Bonesis. This model contains 12 nodes with moderate connectivity and demonstrates key concepts of cellular decision-making processes.
For more details on the Bonesis network and inferences, please checkout this link
Step 1: Load Model Ensemble#
# Load the model path and create AstroLogics object
models_path = 'models/'
with ZipFile("ensemble.zip") as models_zip:
models_zip.extractall(models_path)
model = ast.ensemble(models_path, project_name = 'bonesis')
model.create_simulation()
Simulation object created
The ensemble object is the core component of AstroLogics that handles:
Loading multiple Boolean network models from a directory
Managing simulation parameters and configurations
Coordinating analysis across the model ensemble
Step 2: Simulate the model ensemble#
In this part of the script we first simulate all the BN within the model ensemble. We utilize the MaBoSS engine as the main simulator.
This creates an initial state where all nodes have equal probability (0.5) of being active. This represents a neutral starting condition that allows the system to evolve according to its inherent dynamics.
We then start the simulation using MaBoSS.
MaBoSS (Markovian Boolean Stochastic Simulator) is crucial for the AstroLogics approach because:
It converts Boolean network dynamics into continuous-time Markov processes
Provides probabilistic approximation of complex state transition graphs
Enables analysis of both transient and steady-state behaviors
Scales computationally better than exhaustive state space exploration
# Configure simulation parameters
model.simulation.update_parameters(max_time = 15, sample_count = 1000)
model.simulation.run_simulation()
Start simulation
Simulation completed
Step 3 (Optional) : Trajectory visualization#
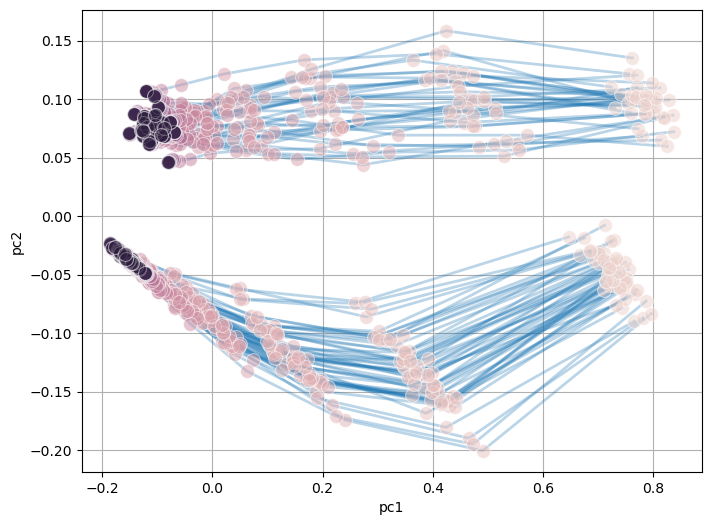
In this steps the simulation trajectories of BNs in the model ensemble can be visualized using PCA. The method allows for a global view of the dynamics of all the models within the model ensembles perform, and may give insight to how the model can potentially be clustered.
model.create_trajectory()
model.trajectory.pca_trajectory()
model.trajectory.plot_pca_trajectory(color = 'timepoint')
Trajectory object created
Step 4: Calculate Distance Matrix#
This step is fundamental to the AstroLogics methodology:
Distance calculation: Compares models based on their endpoint activation probabilities
Euclidean distance: Measures similarity in the final state distributions
Model comparison: Enables identification of models with similar dynamics
In this function calculate_distancematrix, users can select the two options of data used to calculate the distance.
endpoint: The endpoint utilize the node activation probability at the endpoint of MaBoSS simulation. User could also defines thetimepointto define a specific timepoint they want to use to define the distancetrajectory: This options utilize the whole MaBoSS simulation trajectory and thedtwmethod to calculate the distances between models.
model.trajectory.calculate_distancematrix(mode = 'endpoint')
Calculating distance matrix for endpoint simulation...
Distance matrix calculated successfully.
model.trajectory.distance_matrix
| model_id | bn87 | bn66 | bn83 | bn77 | bn36 | bn49 | bn28 | bn38 | bn45 | bn86 | bn24 | bn74 | bn7 | bn13 | bn48 | bn37 | bn57 | bn75 | bn34 | bn40 | bn85 | bn73 | bn31 | bn35 | bn82 | bn1 | bn46 | bn6 | bn29 | bn4 | bn61 | bn16 | bn11 | bn47 | bn44 | bn10 | bn33 | bn14 | bn71 | bn5 | bn56 | bn42 | bn79 | bn60 | bn22 | bn64 | bn39 | bn27 | bn51 | bn15 | bn84 | bn20 | bn53 | bn69 | bn70 | bn2 | bn62 | bn55 | bn67 | bn9 | bn21 | bn54 | bn17 | bn76 | bn43 | bn59 | bn72 | bn30 | bn18 | bn68 | bn23 | bn81 | bn78 | bn0 | bn58 | bn65 | bn52 | bn26 | bn12 | bn80 | bn50 | bn3 | bn19 | bn41 | bn63 | bn32 | bn25 | bn8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| model_id | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| bn87 | 0.000000 | 0.069174 | 0.116516 | 0.120478 | 0.114958 | 0.116790 | 0.083114 | 0.116709 | 0.081951 | 0.027586 | 0.057385 | 0.035014 | 0.040497 | 0.118495 | 0.016852 | 0.012806 | 0.116052 | 0.119327 | 0.119378 | 0.116819 | 0.042202 | 0.117478 | 0.135503 | 0.116675 | 0.026608 | 0.128156 | 0.121050 | 0.123045 | 0.118191 | 0.137666 | 0.117452 | 0.055951 | 0.034234 | 0.120387 | 0.116842 | 0.083618 | 0.115382 | 0.041425 | 0.115365 | 0.120470 | 0.115935 | 0.116035 | 0.004583 | 0.055929 | 0.031496 | 0.073526 | 0.124205 | 0.023022 | 0.128888 | 0.120046 | 0.051118 | 0.045815 | 0.038210 | 0.123709 | 0.138007 | 0.019875 | 0.117149 | 0.120366 | 0.133218 | 0.136642 | 0.079429 | 0.126198 | 0.119038 | 0.035332 | 0.123373 | 0.119473 | 0.019287 | 0.120752 | 0.125348 | 0.045662 | 0.123843 | 0.109403 | 0.124796 | 0.121824 | 0.123746 | 0.057671 | 0.064938 | 0.124455 | 0.123191 | 0.076857 | 0.114965 | 0.039799 | 0.040361 | 0.120669 | 0.134985 | 0.126113 | 0.117222 | 0.053712 |
| bn66 | 0.069174 | 0.000000 | 0.164241 | 0.163150 | 0.159172 | 0.154353 | 0.104723 | 0.153095 | 0.079442 | 0.090344 | 0.043497 | 0.054599 | 0.076400 | 0.150964 | 0.070136 | 0.080716 | 0.163233 | 0.162339 | 0.163297 | 0.157096 | 0.051575 | 0.163829 | 0.156582 | 0.161357 | 0.045727 | 0.171549 | 0.158461 | 0.173277 | 0.151175 | 0.168461 | 0.159518 | 0.096696 | 0.058215 | 0.163162 | 0.153561 | 0.132563 | 0.152938 | 0.072021 | 0.158335 | 0.157480 | 0.162130 | 0.152048 | 0.067838 | 0.080975 | 0.083096 | 0.085680 | 0.157321 | 0.056648 | 0.166346 | 0.169015 | 0.089733 | 0.100737 | 0.068622 | 0.174840 | 0.172479 | 0.079950 | 0.153216 | 0.157025 | 0.170792 | 0.148708 | 0.109599 | 0.146837 | 0.162767 | 0.078941 | 0.166036 | 0.158004 | 0.062809 | 0.176244 | 0.173410 | 0.101528 | 0.165934 | 0.135484 | 0.145482 | 0.166907 | 0.161932 | 0.093043 | 0.111373 | 0.155287 | 0.155547 | 0.030397 | 0.156429 | 0.051059 | 0.072097 | 0.151847 | 0.183761 | 0.158582 | 0.161561 | 0.064312 |
| bn83 | 0.116516 | 0.164241 | 0.000000 | 0.021840 | 0.016393 | 0.030332 | 0.148459 | 0.044933 | 0.149693 | 0.108227 | 0.151456 | 0.134298 | 0.132083 | 0.037749 | 0.121491 | 0.112161 | 0.028810 | 0.048590 | 0.020905 | 0.041866 | 0.139896 | 0.010050 | 0.078797 | 0.040755 | 0.129923 | 0.044068 | 0.031859 | 0.038471 | 0.040012 | 0.070626 | 0.020809 | 0.132291 | 0.130514 | 0.037403 | 0.033377 | 0.123637 | 0.037881 | 0.127122 | 0.025278 | 0.030414 | 0.018841 | 0.037819 | 0.116555 | 0.143059 | 0.121540 | 0.150360 | 0.042720 | 0.125634 | 0.044989 | 0.035567 | 0.128534 | 0.119252 | 0.121408 | 0.044632 | 0.062290 | 0.116897 | 0.037736 | 0.046303 | 0.081762 | 0.081394 | 0.148839 | 0.065054 | 0.034000 | 0.127433 | 0.030806 | 0.051105 | 0.125825 | 0.039433 | 0.039038 | 0.118731 | 0.036235 | 0.168734 | 0.067676 | 0.042720 | 0.058660 | 0.130338 | 0.130303 | 0.051740 | 0.043081 | 0.165375 | 0.028583 | 0.138232 | 0.131875 | 0.053978 | 0.084172 | 0.075379 | 0.026363 | 0.133989 |
| bn77 | 0.120478 | 0.163150 | 0.021840 | 0.000000 | 0.031347 | 0.028337 | 0.141792 | 0.052077 | 0.143670 | 0.110842 | 0.147899 | 0.139718 | 0.133899 | 0.034380 | 0.125988 | 0.116914 | 0.041773 | 0.057966 | 0.011314 | 0.050063 | 0.138138 | 0.021817 | 0.067985 | 0.053740 | 0.131381 | 0.030806 | 0.014832 | 0.042930 | 0.042308 | 0.068007 | 0.016371 | 0.133247 | 0.128814 | 0.036222 | 0.032326 | 0.120054 | 0.045607 | 0.124342 | 0.032863 | 0.014832 | 0.028636 | 0.041920 | 0.120441 | 0.146714 | 0.124382 | 0.144572 | 0.024819 | 0.125766 | 0.023345 | 0.043359 | 0.126428 | 0.122368 | 0.124109 | 0.052335 | 0.040853 | 0.121120 | 0.038013 | 0.045022 | 0.087727 | 0.071021 | 0.148607 | 0.062394 | 0.035511 | 0.130679 | 0.027785 | 0.057520 | 0.129225 | 0.058207 | 0.035285 | 0.122474 | 0.023022 | 0.168030 | 0.067742 | 0.045011 | 0.061725 | 0.126732 | 0.141103 | 0.040669 | 0.027586 | 0.161363 | 0.036797 | 0.136605 | 0.131019 | 0.054074 | 0.098570 | 0.084645 | 0.030133 | 0.130920 |
| bn36 | 0.114958 | 0.159172 | 0.016393 | 0.031347 | 0.000000 | 0.028761 | 0.154289 | 0.037822 | 0.148799 | 0.110229 | 0.150722 | 0.129278 | 0.133080 | 0.029112 | 0.120144 | 0.111968 | 0.031776 | 0.048607 | 0.031978 | 0.038892 | 0.139685 | 0.015676 | 0.078938 | 0.038730 | 0.126554 | 0.056905 | 0.036467 | 0.050518 | 0.026849 | 0.064114 | 0.027165 | 0.135990 | 0.130632 | 0.044668 | 0.030738 | 0.132468 | 0.029517 | 0.128809 | 0.026012 | 0.032866 | 0.025495 | 0.030807 | 0.114631 | 0.142666 | 0.123104 | 0.154141 | 0.045845 | 0.124628 | 0.053801 | 0.044505 | 0.132686 | 0.122985 | 0.117454 | 0.054706 | 0.071504 | 0.117204 | 0.034619 | 0.047516 | 0.082485 | 0.073427 | 0.153350 | 0.052834 | 0.040803 | 0.128062 | 0.032940 | 0.049053 | 0.124279 | 0.044991 | 0.052902 | 0.122253 | 0.047253 | 0.174462 | 0.055738 | 0.050540 | 0.060062 | 0.135056 | 0.128632 | 0.053367 | 0.044860 | 0.161595 | 0.025500 | 0.137903 | 0.133649 | 0.049674 | 0.085087 | 0.068351 | 0.032812 | 0.132681 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| bn41 | 0.120669 | 0.151847 | 0.053978 | 0.054074 | 0.049674 | 0.026359 | 0.151247 | 0.018192 | 0.159210 | 0.121635 | 0.143799 | 0.127502 | 0.126366 | 0.039082 | 0.120427 | 0.118548 | 0.039116 | 0.031875 | 0.047708 | 0.022265 | 0.134401 | 0.058997 | 0.038719 | 0.035025 | 0.129696 | 0.059819 | 0.044369 | 0.055057 | 0.046262 | 0.099391 | 0.039060 | 0.129646 | 0.131482 | 0.034775 | 0.022485 | 0.143914 | 0.023093 | 0.132985 | 0.030431 | 0.046366 | 0.039834 | 0.019299 | 0.121375 | 0.130637 | 0.121863 | 0.147857 | 0.045294 | 0.127759 | 0.063122 | 0.046681 | 0.131888 | 0.123091 | 0.131548 | 0.056157 | 0.076763 | 0.119302 | 0.016746 | 0.017495 | 0.049584 | 0.062019 | 0.141116 | 0.051960 | 0.034273 | 0.123329 | 0.072981 | 0.020865 | 0.122661 | 0.067171 | 0.058297 | 0.122412 | 0.049640 | 0.157963 | 0.037006 | 0.040110 | 0.027339 | 0.135950 | 0.125582 | 0.028207 | 0.039463 | 0.158458 | 0.027218 | 0.133610 | 0.129537 | 0.000000 | 0.075417 | 0.038756 | 0.035015 | 0.141950 |
| bn63 | 0.134985 | 0.183761 | 0.084172 | 0.098570 | 0.085087 | 0.083144 | 0.173727 | 0.066828 | 0.199872 | 0.134536 | 0.173251 | 0.140837 | 0.134480 | 0.100200 | 0.129603 | 0.127597 | 0.057437 | 0.046043 | 0.088702 | 0.058375 | 0.158089 | 0.093188 | 0.104192 | 0.049396 | 0.154444 | 0.096224 | 0.099669 | 0.065215 | 0.101193 | 0.148691 | 0.084735 | 0.132948 | 0.156668 | 0.070498 | 0.081382 | 0.156183 | 0.071652 | 0.158584 | 0.069296 | 0.102196 | 0.070214 | 0.076381 | 0.137201 | 0.131807 | 0.128300 | 0.172218 | 0.106733 | 0.151218 | 0.114599 | 0.057966 | 0.147309 | 0.123150 | 0.157344 | 0.054489 | 0.128938 | 0.126357 | 0.077440 | 0.071169 | 0.042095 | 0.135573 | 0.141506 | 0.117358 | 0.067801 | 0.128583 | 0.114612 | 0.054927 | 0.135074 | 0.053198 | 0.080827 | 0.120814 | 0.091673 | 0.151803 | 0.102181 | 0.061644 | 0.055390 | 0.154903 | 0.105052 | 0.093830 | 0.103097 | 0.197155 | 0.069138 | 0.157623 | 0.145945 | 0.075417 | 0.000000 | 0.053836 | 0.070071 | 0.176170 |
| bn32 | 0.126113 | 0.158582 | 0.075379 | 0.084645 | 0.068351 | 0.058245 | 0.169613 | 0.033524 | 0.179776 | 0.131951 | 0.155938 | 0.125634 | 0.130354 | 0.068652 | 0.122604 | 0.123425 | 0.051556 | 0.035109 | 0.077148 | 0.035428 | 0.144625 | 0.081552 | 0.071031 | 0.037890 | 0.137460 | 0.090638 | 0.079022 | 0.072453 | 0.069290 | 0.123506 | 0.068723 | 0.135493 | 0.143963 | 0.060665 | 0.054644 | 0.162379 | 0.041434 | 0.148263 | 0.052766 | 0.080086 | 0.060870 | 0.045227 | 0.127258 | 0.128036 | 0.126758 | 0.163965 | 0.082446 | 0.138182 | 0.098699 | 0.061542 | 0.144792 | 0.128321 | 0.141169 | 0.067412 | 0.113545 | 0.123190 | 0.049013 | 0.048068 | 0.038514 | 0.092114 | 0.146064 | 0.075145 | 0.058354 | 0.125693 | 0.099441 | 0.030407 | 0.125804 | 0.069261 | 0.082750 | 0.126598 | 0.081440 | 0.161268 | 0.055085 | 0.059277 | 0.039025 | 0.151512 | 0.112580 | 0.066346 | 0.076959 | 0.171681 | 0.048350 | 0.144003 | 0.139165 | 0.038756 | 0.053836 | 0.000000 | 0.059150 | 0.158522 |
| bn25 | 0.117222 | 0.161561 | 0.026363 | 0.030133 | 0.032812 | 0.019925 | 0.143524 | 0.031496 | 0.155843 | 0.110887 | 0.147180 | 0.132427 | 0.125208 | 0.040497 | 0.118924 | 0.112423 | 0.016155 | 0.028496 | 0.019900 | 0.024039 | 0.135610 | 0.034900 | 0.058583 | 0.027166 | 0.130947 | 0.034713 | 0.029933 | 0.024021 | 0.047666 | 0.090813 | 0.015362 | 0.124305 | 0.129356 | 0.012166 | 0.021095 | 0.124936 | 0.028914 | 0.127322 | 0.010770 | 0.033257 | 0.008944 | 0.027186 | 0.118051 | 0.133675 | 0.117017 | 0.144489 | 0.038053 | 0.125782 | 0.045332 | 0.017889 | 0.124346 | 0.114219 | 0.128425 | 0.029069 | 0.061196 | 0.114516 | 0.022159 | 0.022204 | 0.058207 | 0.079246 | 0.137557 | 0.066940 | 0.008062 | 0.121407 | 0.052745 | 0.029968 | 0.122674 | 0.041231 | 0.027477 | 0.113657 | 0.025534 | 0.154654 | 0.061879 | 0.018439 | 0.033526 | 0.127283 | 0.124346 | 0.034351 | 0.035819 | 0.165039 | 0.016852 | 0.134503 | 0.126783 | 0.035015 | 0.070071 | 0.059150 | 0.000000 | 0.138744 |
| bn8 | 0.053712 | 0.064312 | 0.133989 | 0.130920 | 0.132681 | 0.133420 | 0.078339 | 0.141131 | 0.028302 | 0.055100 | 0.051381 | 0.072739 | 0.077672 | 0.129027 | 0.067060 | 0.062201 | 0.142573 | 0.149452 | 0.133791 | 0.143285 | 0.051846 | 0.131666 | 0.147811 | 0.146192 | 0.039102 | 0.140851 | 0.130545 | 0.147584 | 0.129677 | 0.131883 | 0.133252 | 0.089152 | 0.036729 | 0.141866 | 0.134324 | 0.087115 | 0.137848 | 0.035228 | 0.137426 | 0.128965 | 0.137746 | 0.136297 | 0.050754 | 0.097658 | 0.072973 | 0.070221 | 0.130843 | 0.036042 | 0.132789 | 0.146369 | 0.066332 | 0.084817 | 0.036620 | 0.151951 | 0.137175 | 0.068191 | 0.136385 | 0.141989 | 0.167511 | 0.135248 | 0.109197 | 0.132684 | 0.141411 | 0.078559 | 0.128794 | 0.147299 | 0.063726 | 0.151559 | 0.144336 | 0.086718 | 0.137361 | 0.138434 | 0.138741 | 0.146751 | 0.151565 | 0.063016 | 0.118440 | 0.137419 | 0.131457 | 0.048518 | 0.137390 | 0.048918 | 0.062418 | 0.141950 | 0.176170 | 0.158522 | 0.138744 | 0.000000 |
88 rows × 88 columns
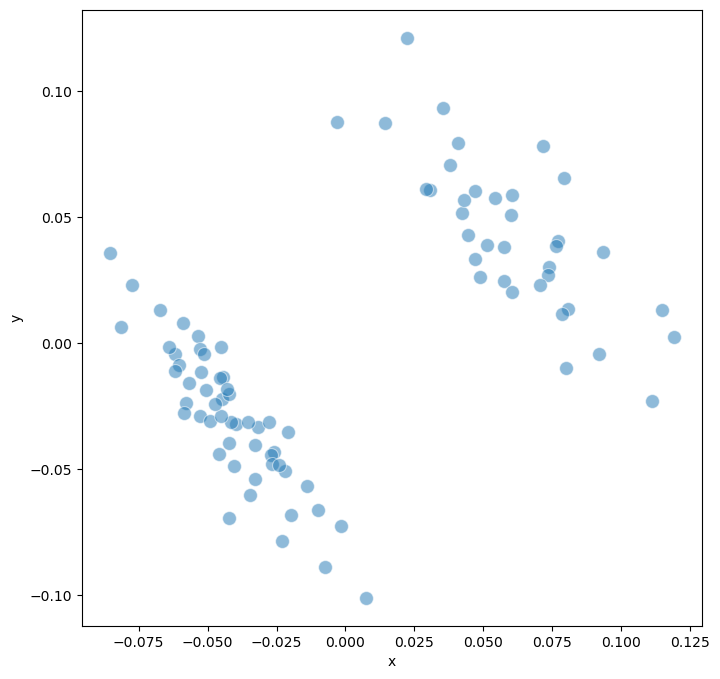
Step 5: Dimensionality Reduction and Visualization#
Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) projects the high-dimensional distance matrix onto a 2D plane, preserving relative distances between models. This visualization reveals:
Model clusters: Groups of models with similar dynamics
Outliers: Models with unique behavioral patterns
Gradient patterns: Continuous transitions between model types
# Perform MDS (Multidimensional Scaling) for visualization
model.trajectory.calculate_MDS()
model.trajectory.plot_MDS(s = 100, fig_size = (8,8))
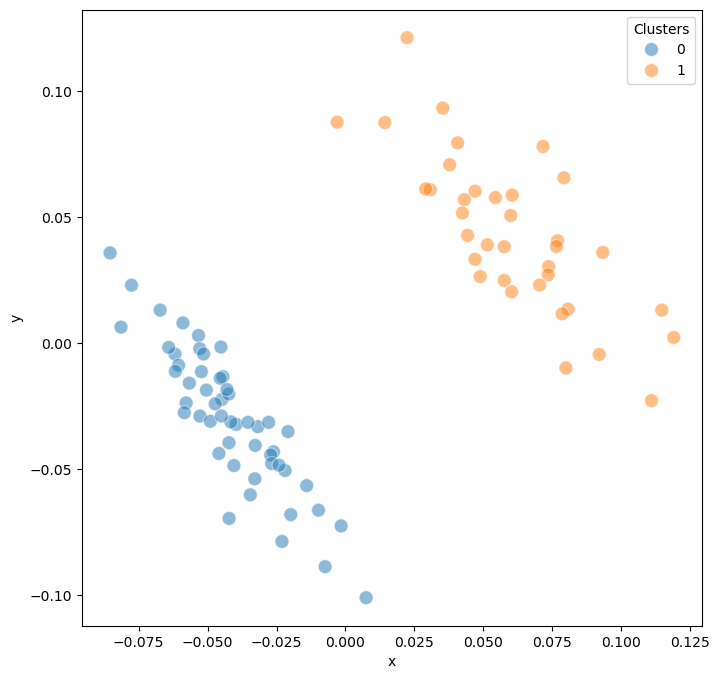
Step 6: Model Clustering#
Clustering reveals distinct groups within the model ensemble. In the CNS differentiation example, we found 2 major clusters corresponding to different attractor groups, representing distinct cellular fate decisions.
model.trajectory.calculate_kmean_cluster(n_cluster = 2,
random_state = 0)
Calculated k-means clustering with 2 clusters.
model.trajectory.plot_MDS(s = 100, fig_size = (8,8),plot_cluster = True)
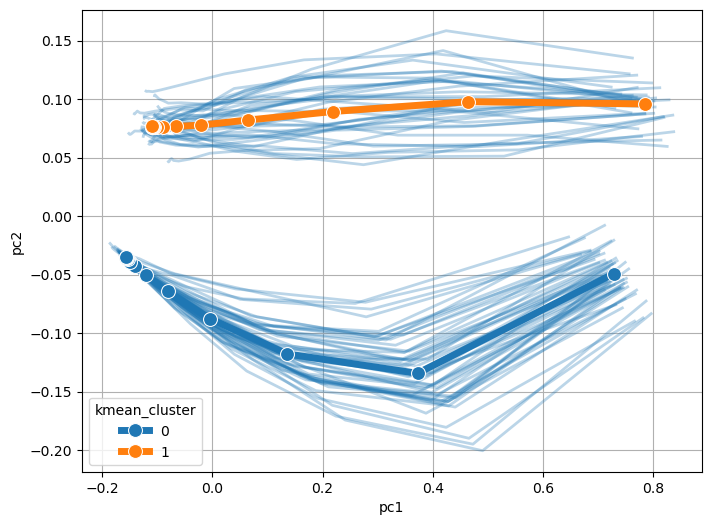
Step 7 (Optional) : Trajectory Analysis#
In this step, we projected the calculated clusters onto the trajectory PCA in the step 3.
model.trajectory.plot_pca_trajectory(plot_cluster=True)
Step 8: Logic Function Analysis#
This step implements the logical function evaluation component of AstroLogics:
Converts Boolean equations to Disjunctive Normal Form (DNF)
Creates feature matrices comparing logical rules across models
Identifies constant, varied, and marker clauses
model.create_logic()
model.logic.model_logic
model.logic.create_flattend_logic_clause()
Loading models logics
Concatenate results into matrix
Logic object created
Flatten models logic clauses
Concatenate results into matrix
Flattend logic clause created
Step 9 : Calculate statistic of Logic features (clauses)#
In this steps, we have already featurized the logical equations into model logics or clauses.
We can then integrate the clusters obtained from the trajectory analysis into the .logic and perform chi-square statistical test to categorize logic features (clauses) into 3 major groups
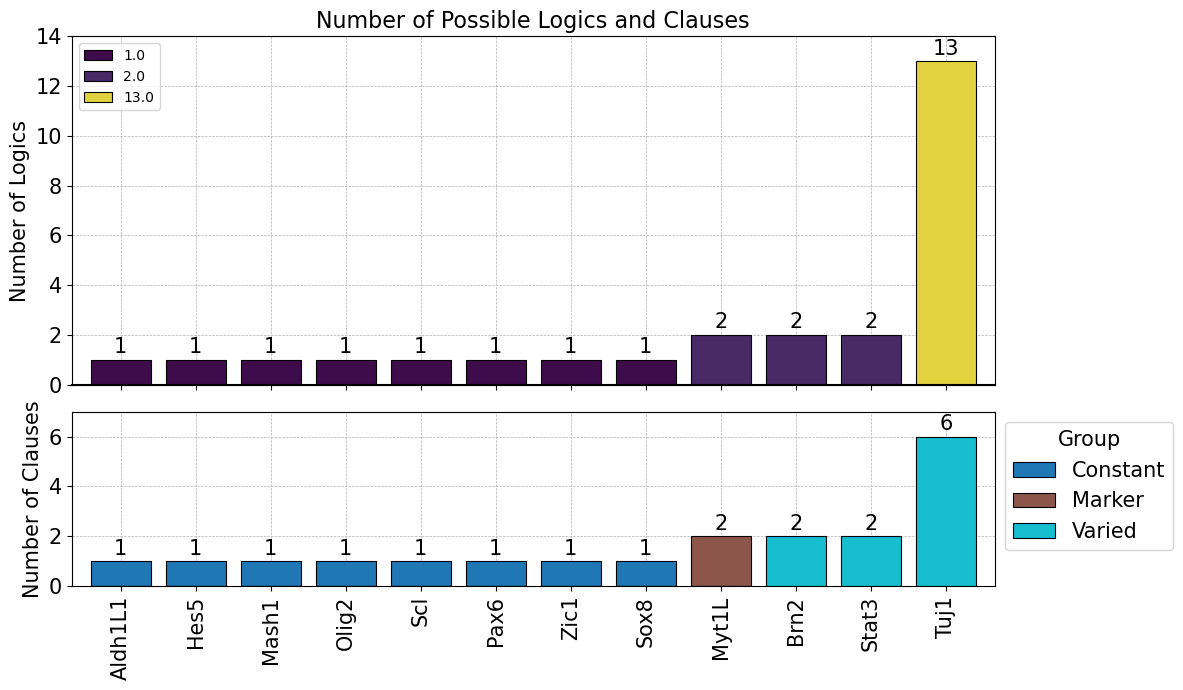
Constatnt : core regulatory features that appears across BNs in the model ensemble
Varied : Features that may differ between individual BNs but show no statistical significant
Marker : Key discriminatory features that statistically distinguish between different model clusters.
We can define the p-value of the chi-square test using the function pval_threshold.
model.logic.map_model_clusters(model.trajectory.cluster_dict)
model.logic.calculate_logic_statistic(pval_threshold = 0.0001)
Model clusters mapped to logic clauses
The results of the analysis can be visualized in the form of Manhattan Plot shown below.
model.logic.plot_manhattan()
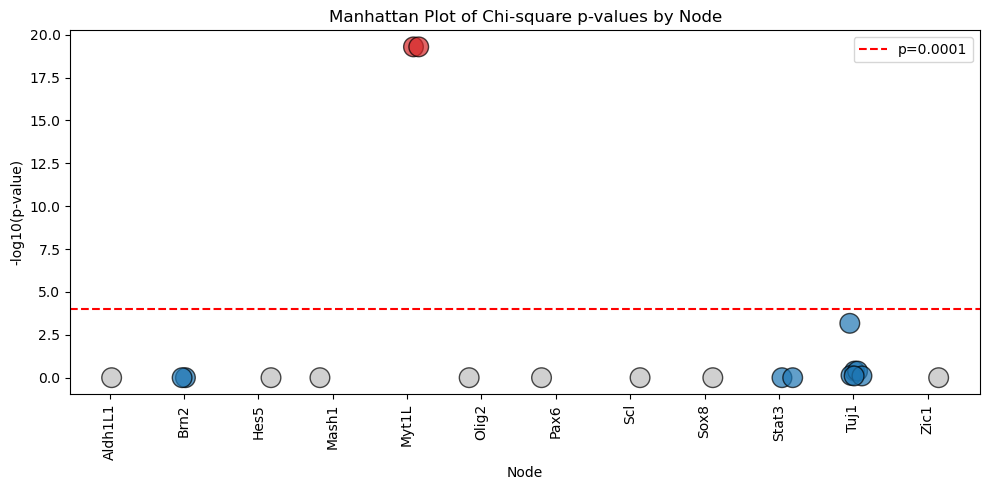
Or the results can be summarized into the barplot shown here
model.logic.plot_logicstat_summary()
Step 9: Advanced Trajectory Analysis#
These visualizations help identify:
Most variable nodes: Components showing greatest differences between models
Critical regulators: Nodes whose activity patterns distinguish model clusters
Temporal patterns: How specific nodes behave over simulation time
In this first plot, we check what are the features that shows the highest variance in their dynamics accross simulation. We calculate the variance of node activation probabily of all BNs in the model ensemble across all timepoints and plotted using the heatmap.
model.trajectory.plot_trajectory_variance()
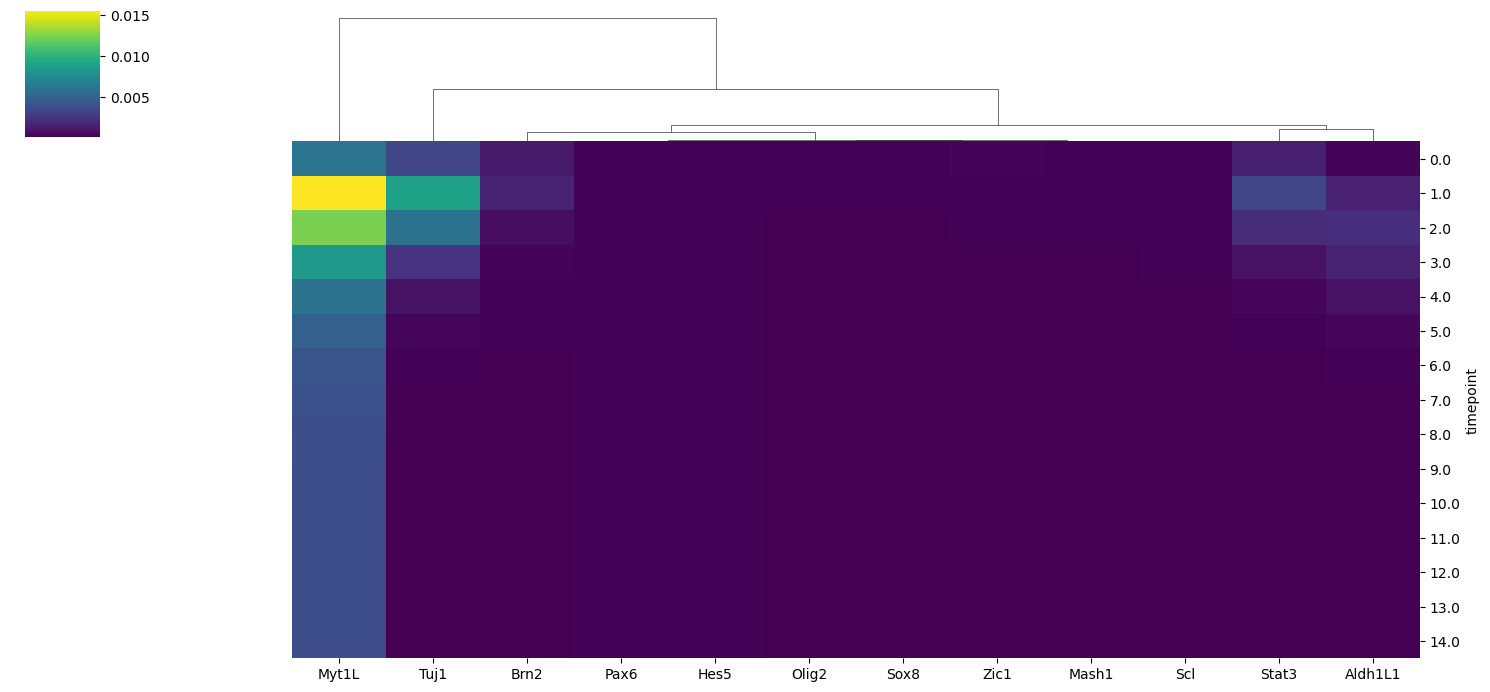
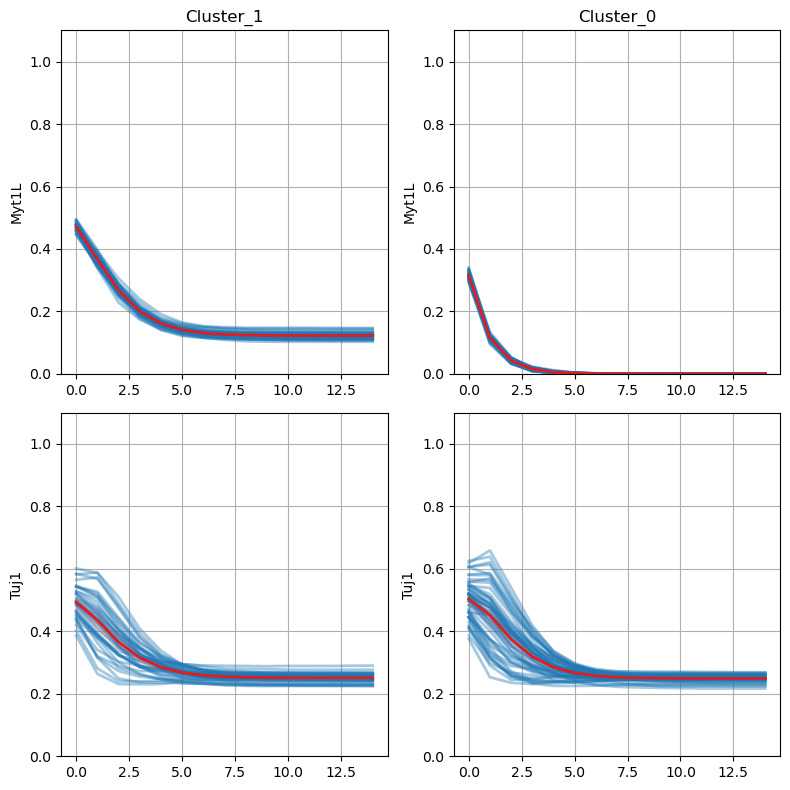
We identify the key node of interest (Myt1L) which shows the highest variance along the timepoints. Finally, we could visualize the dynamics of this node between two identified clusters using the lineplot.
model.trajectory.plot_node_trajectory(node = ['Myt1L', 'Tuj1'])
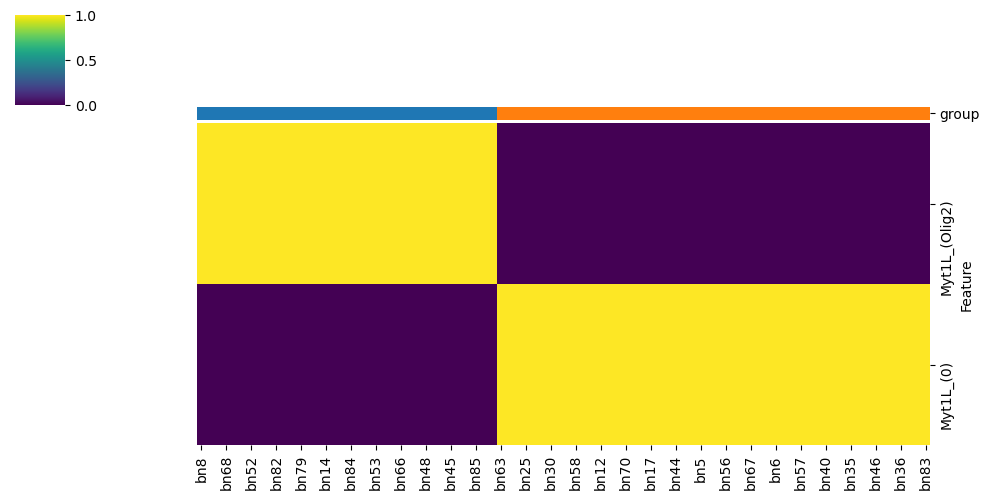
Step 10: Logic Feature Heatmap#
This analysis typically reveals that Myt1L is the key distinguishing node between clusters:
Cluster 0: Myt1L regulated by Olig2
Cluster 1: Myt1L deactivated (value = 0)
model.logic.plot_node_logic_heatmap(node = ['Myt1L'],
fig_size = (8, 8))
<Figure size 800x800 with 0 Axes>
Key Findings and Biological Interpretation#
The AstroLogics analysis of the CNS differentiation model reveals:
Dynamic Properties#
Two main clusters representing different developmental pathways
Distinct attractor landscapes corresponding to different cell fates
Conserved transient patterns showing robust developmental trajectories
Logical Properties#
Myt1L as key regulator: The primary distinguishing factor between clusters
Regulatory mechanisms: Different logical rules governing cell fate decisions
Constant vs. variable features: Core vs. flexible regulatory elements
Applications and Extensions#
Benchmarking Model Synthesis Methods#
AstroLogics can compare models generated by different synthesis tools:
Bonesis vs BN-sketch performance
Constraint sensitivity analysis
Solution space characterization
Complex Network Analysis#
For larger networks (like the cancer invasion model with 32 nodes):
Computational advantages: MaBoSS simulation vs. exhaustive attractor calculation
Scalability: Handling thousands of models efficiently
Approximation quality: Balancing accuracy with computational feasibility
Transient Dynamics Focus#
Unlike methods focusing only on attractors, AstroLogics captures:
Dynamic Time Warping: Comparing trajectory shapes and timing
Intervention opportunities: Identifying critical transition points
Pathway analysis: Understanding how systems reach their endpoints
Conclusion#
This tutorial demonstrates how AstroLogics provides a comprehensive framework for Boolean network ensemble analysis. By combining dynamic simulation with logical feature analysis, it offers insights into both the “what” (final states) and “how” (pathways) of cellular decision-making processes.
The framework addresses the critical need for model evaluation and comparison in an era of increasingly sophisticated Boolean network synthesis methods, supporting the transition from single models to ensemble-based understanding of biological systems.
